
You may assume the uncertainty in position is negligible. Trigonometric functions, quadratic functions where the coefficient B ≠ 0, and various other functions cannot be analyzed using linearization.The data set "calibration.txt" shows the _reported_ position of a rotational sensor (in units of $\frac \cos(\omega t + \phi) + \varphi $$įind the resonant frequency $\omega$ and the damping constant $\beta$ for this apparatus. Data that matches many interesting functional relationships cannot be easily linearized. Putting an equation in the form g( y) = A f( x)+B may require a lot of cleverness. A graph of linearized data is a straight line so the nature of the relationship between theĢ. However, it may be difficult to interpret.ġ. The uncertainty in the linearized parameter is easy to obtain using a basic least squaresĪnalysis. In particular, log or log-log paper might be useful.ģ. Graphing can be performed more easily than for other methods.
#LOGGER PRO UNCERTAINTY FITTED PARAMETERS MANUAL#
If a function can be linearized and if no computer is available, then manual calculations and Many older scientists and teachers are comfortable with it. Menu The coefficients A and B will be calculated for you using a Linear Regression analysis along with the Root Mean Square Error (RSME).ġ. If the linearized data appear to lie along a line, then choose Linear Fit in the Analyze Add the sensor to Logger Pro by going to Experiment Set Up Sensors Show All Interfaces or by clicking on the LabPro icon in the upper left corner. Logger pro will draw the linear best fit. Measuring the phase shift between two different.
#LOGGER PRO UNCERTAINTY FITTED PARAMETERS HOW TO#
I have no idea how to incorporate that into the uncertainty given by the following model: I Iocos2( o) + c I I o c o s 2 ( o) + c. and select the desired equation such as Linear, Natural Exponent, or several other options. If the graph is not linear try finding other functions g( y) and/or f( x). If you make a single measurement, you can estimate the uncertainty based on the tool you used (e.g. I have recorded the uncertainty in the measurement of the intensity and degree of rotation to be ☑.5 ± 1.5 and ±5 ± 5 respectively. Given a data sample, we use the fit method of SciPy to extract the parameters of that distribution that best fit the data. Therefore, an automatic way to fit many distributions to the data would be useful, which is what is implemented here. Use New Calculated Column in Logger Pro to create new variables g( y) and f( x). Yet, the parameters of the distribution are not known and there are lots of distributions. The units 0 these values are in whatever units the Logger Pro sofiware. Enter the distance/length into the appropriate parameter box, when. Inaccurate distance measurements will lead to bad velocity and acceleration data. Take special care in measuring the appropriate distance/length. Enter or record the x, y data in Logger Pro. When the fit is performed on actual data, the fit parameters have the following. The Logger Pro sensor files for use with Photogates can be found in the Experiments>Probes & Sensors>Photogates folder. Where p is a non-zero number, then g( y) = y and f( x) = xĢ. Variables can be put in the form g( y) = A f( x)+B, then linearization is possible. x suggests that the equation linking these If theory or the shape of a graph of y vs. For example the local maxima of a damped oscillation can be modeled but not fit without a lot of extra work.ġ. Envelopes of functions that can be seen visually cannot be fit without creating a new data Sometimes when fitting many cycles of a sinusoidal function, fitting must be repeatedĤ. Fitting does not help users learn how each coefficient in an equation affects the graph ofģ.

Fitting does not help users focus on what shapes various analytic functions have. Fitting usually takes less time than modeling, 2. Close the window with the small graph you matched. With the y-intercept not equals to 0 m/s/s, it tells us that there are uncertainties involved in the process of the experiment. If the match is not good, try picking or entering another function (or repeat the fitting if youĪre matching a sine, cosine or tangent function).Ħ. A linear fitted line should appear on the graph. Select the linear fit toolbar icon (a straight red line overlaying a blue curve). The coefficients will be calculated for you using a least squares analysis along with theĥ. To get best fit line on the graph: Click and drag on the main graph to select all the data points you want fitted (this is usually all of them). In the Analyze menu choose Curve Fit, then the analytic function you think will match. With Blockly, students can create custom data collection parameters. Insert a graph of the two variables being analyzed (with Connect Points turned off underģ. If students are collaborating on a lab activity across devices, they can set up a.

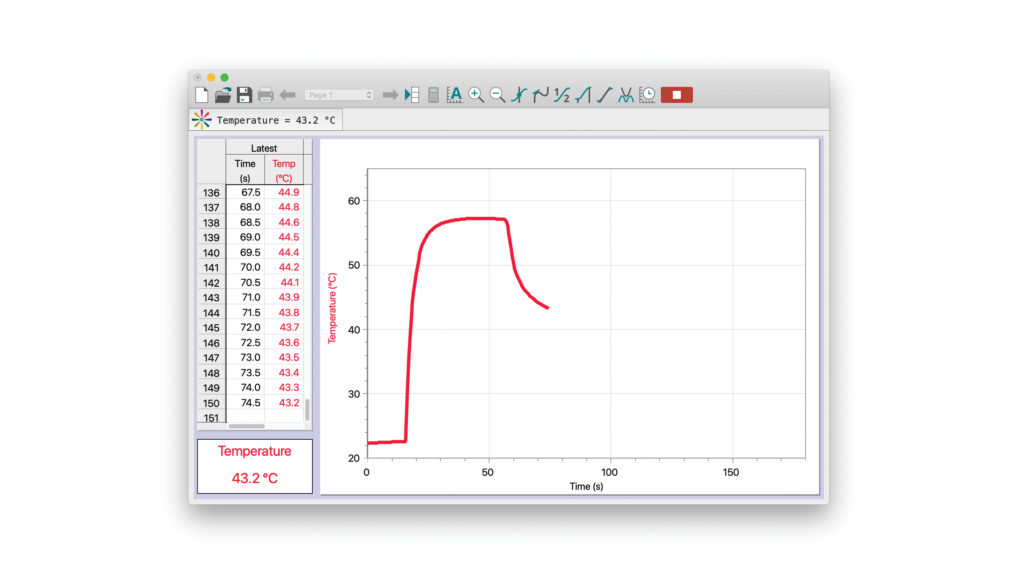
Logger Pro Modeling, Fitting, and Linearizationġ.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
